Depo-Provera, typically used for contraception in women, isn’t approved for male use. However, research explores its potential applications in treating prostate cancer and other conditions. Prescribing information varies significantly depending on the specific medical context and individual patient needs. Therefore, obtaining precise dosage recommendations requires direct consultation with a qualified medical professional.
Crucially, self-medicating with Depo-Provera is dangerous. Incorrect dosage can lead to serious health complications. A doctor will consider factors like body weight, overall health, and the specific condition being treated before determining an appropriate dosage (if any). They’ll explain the potential benefits and risks thoroughly.
Remember, this information is for educational purposes only and doesn’t substitute professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new medication, including off-label uses of drugs like Depo-Provera. They can provide personalized guidance and monitor your progress safely and effectively.
- Depo Provera for Men: Dosage and Considerations
- Depo-Provera’s Current Unapproved Use in Men
- Off-Label Use and Associated Risks
- Monitoring and Precautions
- Specific Risks
- Potential Benefits and Applications in Men (Research Focus)
- Investigating Side Effects and Long-Term Impacts
- Beyond Contraception: Exploring Other Applications
- Dosage Regimens Explored in Research Studies
- Intramuscular Injection Studies
- Challenges and Considerations
- Further Research Needs
- Monitoring and Side Effects in Male Patients
- Common Side Effects
- Less Frequent, but Important Side Effects
- Monitoring Schedule & Potential Issues
- Reporting Changes
- Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Importance of Individual Assessment
Depo Provera for Men: Dosage and Considerations
Depo-Provera is not currently FDA-approved for male contraception. Therefore, there’s no established dosage for men. Any use would be off-label and under the strict supervision of a physician.
However, research explores its potential use in men, and studies typically examine varying dosages to determine efficacy and side effects. These dosages aren’t standardized and vary widely between studies. Never attempt to self-administer Depo-Provera without direct medical guidance.
- Potential Dosage Studies: Research explores a range of dosages, from single injections to repeated administrations at different intervals. These studies analyze hormonal changes and efficacy rates following different injection schedules.
- Individualized Approach: If a doctor considers Depo-Provera in a clinical trial setting, the dosage will be highly personalized. It will depend on factors such as age, weight, and overall health.
Before considering any off-label use:
- Consult a specialist: Discuss all available options with a qualified endocrinologist or reproductive health specialist experienced in male hormonal contraception.
- Understand the risks: Be fully aware of potential side effects, including decreased libido, weight gain, mood changes, and bone density changes.
- Discuss alternatives: Explore other male contraceptive methods, such as vasectomy or condoms, which are safe and proven.
- Monitor your health: Regular blood tests and checkups are crucial if you participate in a clinical trial using Depo-Provera.
Remember: The safety and efficacy of Depo-Provera for men require further research. This information is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice.
Depo-Provera’s Current Unapproved Use in Men
Depo-Provera is not FDA-approved for use in men. However, off-label use exists, primarily for managing advanced prostate cancer and sometimes for managing hypersexuality in certain cases.
Off-label use means a doctor might prescribe it for a condition other than what the drug is officially approved for. This is done based on clinical judgment and the patient’s specific circumstances. It is crucial to understand that research on Depo-Provera’s efficacy and safety for these specific uses in men is limited.
If considering this treatment option, detailed discussions with a qualified endocrinologist or oncologist are necessary. They will assess individual health risks and benefits, considering potential side effects like decreased libido, weight gain, and bone density changes. Regular monitoring of hormone levels and bone health is highly recommended if off-label use is pursued. Always discuss all potential risks and benefits thoroughly.
Remember, self-medicating with Depo-Provera is dangerous and strongly discouraged. Consult a medical professional for any health concerns and treatment options.
Off-Label Use and Associated Risks
Depo-Provera, while approved for women’s contraception, lacks FDA approval for male use. Any off-label application carries inherent risks. These include, but aren’t limited to, potential hormonal imbalances leading to decreased libido, gynecomastia (breast development in men), weight gain, and mood changes. Prolonged use may also affect bone density and increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
Monitoring and Precautions
Regular blood tests to monitor hormone levels are crucial during any off-label use. Men considering this option should discuss potential risks and benefits thoroughly with their doctor. A complete physical exam, including blood work, should precede any treatment. Open and honest communication with the physician regarding any symptoms is absolutely necessary for timely intervention. Self-medication is strongly discouraged.
Specific Risks
Reduced Sperm Production: A significant risk is a decrease in sperm count, potentially leading to temporary or even permanent infertility. This effect’s duration and severity vary considerably among individuals. Fertility recovery after cessation of Depo-Provera is not guaranteed and the timeline is unpredictable.
Potential Benefits and Applications in Men (Research Focus)
Current research primarily focuses on Depo-Provera’s potential for male contraception. Studies explore its efficacy in suppressing sperm production, aiming to develop a long-acting, injectable contraceptive for men comparable to Depo-Provera’s existing use in women. Researchers are investigating optimal dosage and administration schedules to maximize efficacy while minimizing side effects.
Investigating Side Effects and Long-Term Impacts
Ongoing trials assess the impact of Depo-Provera on testosterone levels, libido, and other potential side effects in men. Scientists are carefully monitoring participants for any adverse health consequences, paying close attention to cardiovascular health and bone density. This research aims to identify any potential risks associated with long-term use and refine administration protocols to mitigate them. Data analysis will guide recommendations for safe and effective application.
Beyond Contraception: Exploring Other Applications
Beyond contraception, preliminary research suggests potential applications of Depo-Provera in managing certain hormone-related conditions in men. Studies are exploring its use in treating prostate cancer and other conditions where hormone suppression may be beneficial. However, this remains an area of early-stage investigation, requiring further research to confirm its viability and safety.
Dosage Regimens Explored in Research Studies
Research on Depo-Provera for men has explored various dosage regimens, primarily focusing on intramuscular injections. Results vary depending on the study design and participant characteristics.
Intramuscular Injection Studies
- One study investigated a 150mg intramuscular injection every 3 months. This regimen showed significant suppression of testosterone levels in the majority of participants.
- Another trial evaluated a 100mg dose administered every 2 months. This dosage yielded lower testosterone suppression compared to the 150mg regimen but still demonstrated efficacy in some participants.
- Several studies examined the effects of varying injection frequencies, ranging from monthly injections to injections every six months. Data revealed a correlation between frequency and the degree of testosterone suppression.
It’s important to note that individual responses to Depo-Provera vary widely. Factors such as age, weight, and overall health can influence the effectiveness of the medication. Therefore, individualized dosage adjustments might be needed for optimal results.
Challenges and Considerations
- Maintaining consistent adherence to injection schedules is crucial for sustained testosterone suppression. Missed injections can significantly impact the treatment’s effectiveness.
- Long-term effects of Depo-Provera on male reproductive health require further investigation. Studies are ongoing to evaluate potential long-term risks and benefits.
- Monitoring testosterone levels is recommended during treatment. Regular blood tests help physicians assess the medication’s efficacy and make necessary dosage adjustments.
Further Research Needs
More research is needed to identify optimal dosage regimens for men, considering factors like individual characteristics and specific treatment goals. Larger, longer-term studies with diverse participant populations will further refine our understanding of Depo-Provera’s application in men.
Monitoring and Side Effects in Male Patients
Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor hormone levels, specifically testosterone and hematocrit. These tests should be scheduled at least every 3 months to detect any significant changes. Frequency may need to increase based on individual responses.
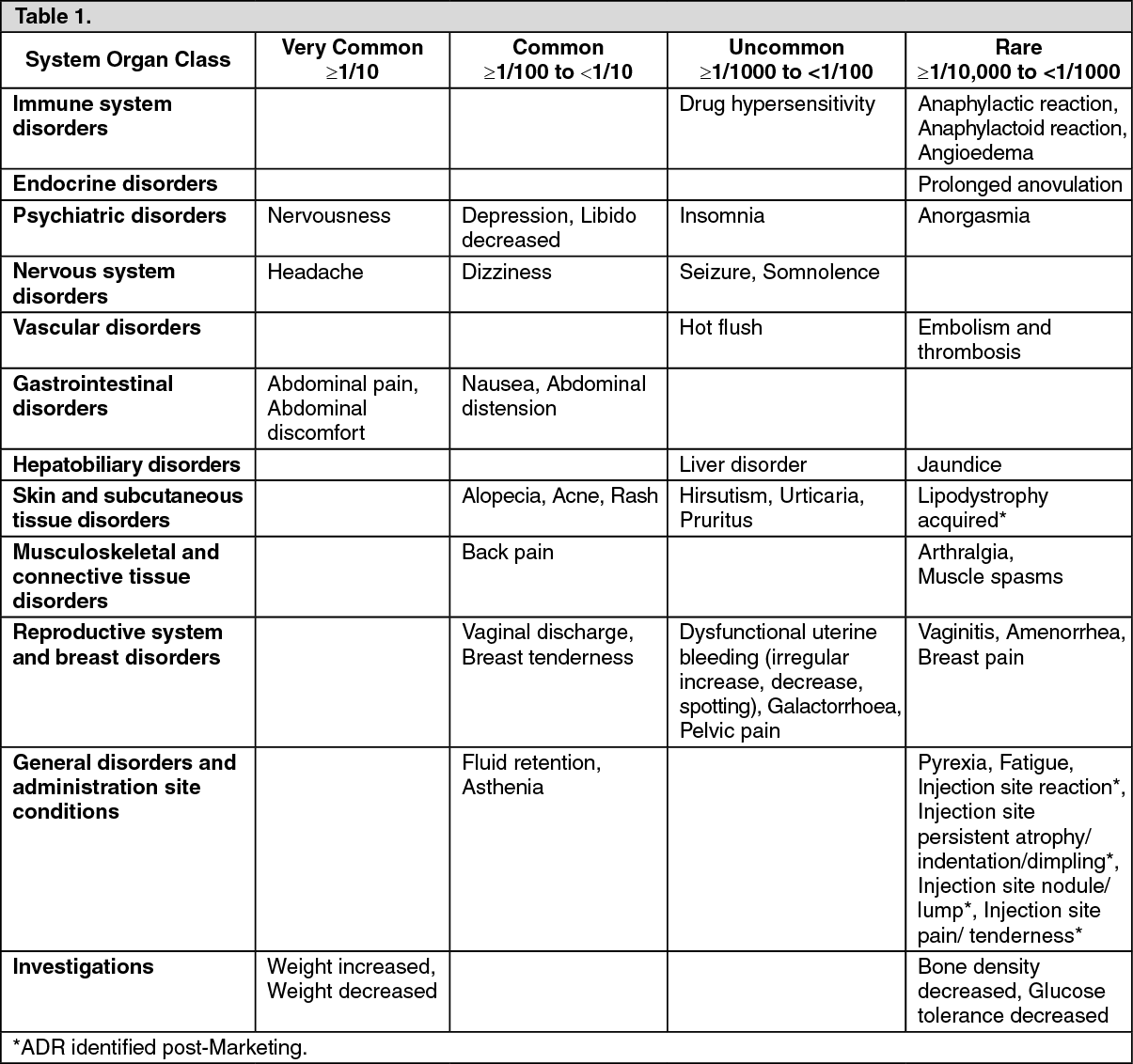
Common Side Effects
Expect some changes. Decreased libido is frequently reported. Weight gain and mood changes, including irritability, depression, and decreased energy, can also occur. Gynecomastia (breast enlargement) is a possibility, although less common. Hair loss and acne are other potential side effects.
Less Frequent, but Important Side Effects
While less common, serious side effects warrant immediate medical attention. These include significant changes in vision, severe headaches, chest pain, or shortness of breath. Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of these.
Monitoring Schedule & Potential Issues
| Monitoring Point | Tests | Potential Issue Indication |
|---|---|---|
| Month 1-3 | Testosterone, Hematocrit, Liver function tests | Significant drop in testosterone, anemia, liver damage |
| Month 3-6 | Testosterone, Hematocrit, Complete Blood Count (CBC) | Ongoing libido decrease, persistent anemia, changes in blood cell counts |
| Months 6+ | Testosterone, Hematocrit, Lipid panel, Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) | Persistent low testosterone, anemia, cholesterol changes, prostate issues |
Reporting Changes
Open communication with your doctor is crucial. Report any changes, even if seemingly minor, to ensure timely adjustment of treatment or management of side effects. Your health and well-being are paramount.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional: Importance of Individual Assessment
Seek personalized advice. Don’t rely on online information alone. A doctor will assess your specific health needs and discuss potential risks and benefits related to Depo-Provera or any other treatment option.
Medical history review is key. Your doctor will review your complete medical history, including allergies, current medications, and existing health conditions. This detailed review helps determine suitability for Depo-Provera.
Proper testing may be required. Blood tests and physical examinations help evaluate your overall health before starting Depo-Provera. This ensures the treatment is safe and effective for you.
Discuss potential side effects. Your healthcare provider will explain potential side effects, such as weight changes, mood alterations, and irregular bleeding. Openly discussing these concerns ensures informed decision-making.
Long-term planning matters. Depo-Provera affects hormone levels. Your doctor will help you create a long-term plan that considers your fertility goals and any potential impact on your health.
Regular checkups are recommended. Monitor your health closely while using Depo-Provera. Scheduled checkups allow your doctor to address any concerns and adjust treatment as needed.
Alternative options will be explored. If Depo-Provera is unsuitable, your physician will discuss alternative contraception methods tailored to your specific circumstances.