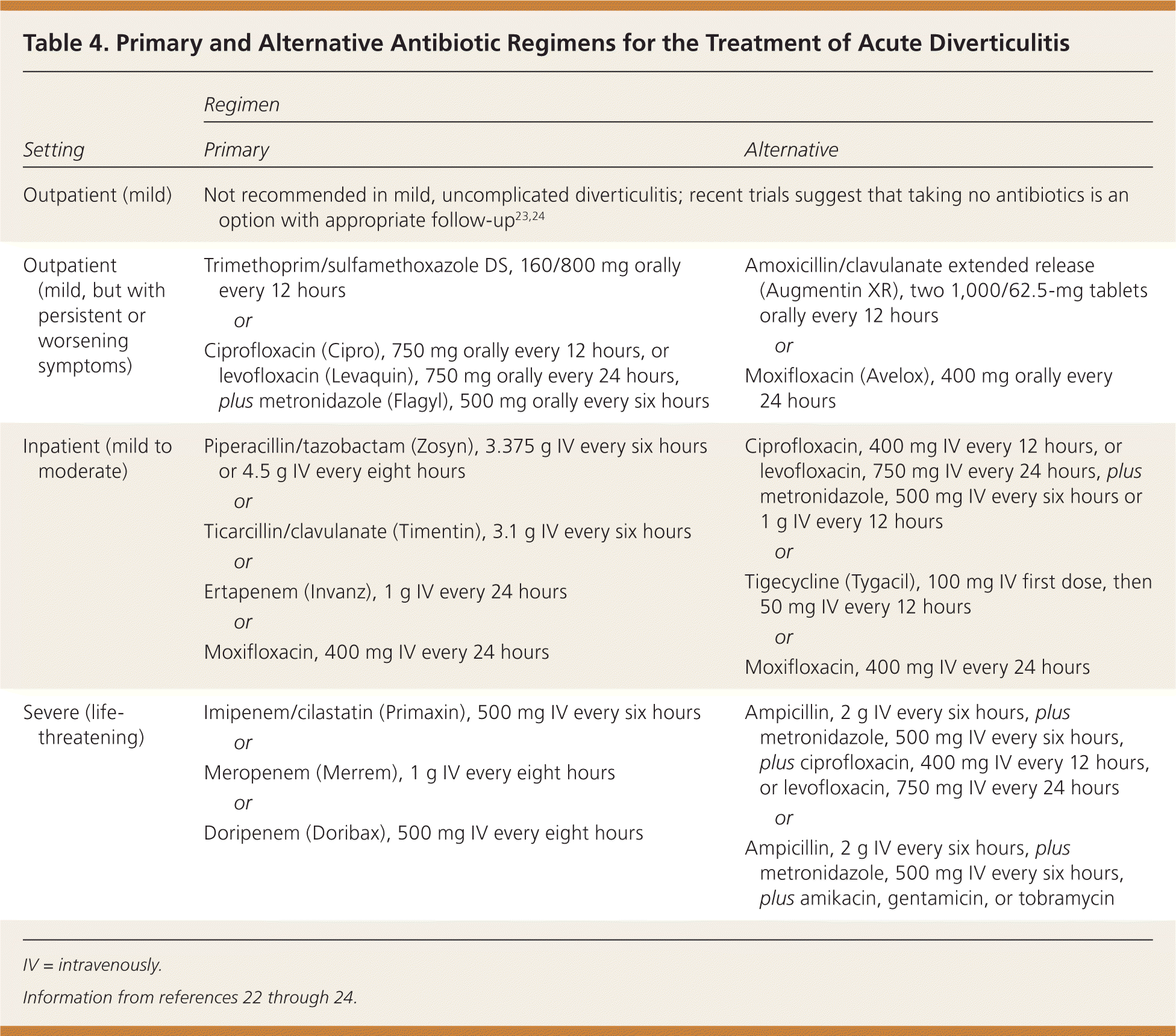
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and Metronidazole (Flagyl) are frequently prescribed antibiotics for uncomplicated diverticulitis. This combination targets the common bacteria causing infection. However, remember that antibiotic resistance is a growing concern, so always follow your doctor’s instructions precisely regarding dosage and duration.
While this antibiotic duo often proves effective, it’s crucial to understand that severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics or hospitalization. Factors such as the extent of the infection, the presence of complications (like abscesses or fistulas), and your overall health determine the best treatment approach. Your physician will assess your individual needs.
Always consult your doctor before starting any antibiotic treatment. They will conduct a thorough evaluation to confirm the diagnosis and determine if Cipro and Flagyl are appropriate for your specific situation. Self-treating can be dangerous and may lead to more serious complications. Your doctor can also advise on potential side effects and alternative treatment options if needed.
Beyond antibiotics, managing diverticulitis involves dietary changes. A high-fiber diet is recommended to promote regular bowel movements and reduce straining, which can exacerbate the condition. Your doctor may also suggest lifestyle adjustments, such as increasing fluid intake and managing stress. Following these guidelines alongside antibiotic therapy optimizes your recovery.
Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole (Flagyl) for Diverticulitis: A Closer Look at Efficacy and Side Effects
For uncomplicated diverticulitis, a combination of Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole often provides effective treatment. Studies show significant improvement in symptoms within a week for most patients. However, resistance to these antibiotics is a growing concern, necessitating careful consideration of their use.
Ciprofloxacin targets Gram-negative bacteria, while Metronidazole tackles anaerobic bacteria commonly involved in diverticulitis. This dual approach addresses a broader spectrum of pathogens. Typical treatment duration is seven to ten days.
While generally well-tolerated, side effects can occur. Ciprofloxacin can cause nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Metronidazole might lead to metallic taste, nausea, and dark urine. Serious, though rare, side effects include Clostridium difficile infection (C. diff) and allergic reactions. Patients should report any unusual symptoms to their doctor immediately.
Alternatives exist for patients with allergies or antibiotic resistance. Amoxicillin-clavulanate is a viable option. For severe cases, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be required. Always follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve.
Before starting treatment, discuss potential drug interactions with your physician. This is especially important for those taking other medications. Regular monitoring of your symptoms is also key to ensuring successful treatment and preventing complications.
Practical Considerations: Dosage, Duration, and When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Ciprofloxacin and metronidazole dosages vary depending on the severity of your diverticulitis and your doctor’s assessment. Typical Ciprofloxacin dosages range from 500mg to 750mg twice daily, while Metronidazole is often prescribed at 500mg to 750mg twice daily. Your healthcare provider will determine the precise dosage and duration of treatment, usually for 7-10 days. Always follow your prescribed regimen carefully. Do not adjust dosages or stop treatment early without consulting your physician.
Monitoring Your Condition
Closely monitor your symptoms. Improvement should be noticeable within a few days. If your symptoms worsen or fail to improve, contact your doctor immediately. This is particularly important if you experience high fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), severe abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, or bloody stools. These could indicate a more serious complication like an abscess or perforation, requiring prompt intervention.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Care
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- High fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C)
- Severe abdominal pain that worsens rapidly
- Inability to pass gas or have a bowel movement
- Bloody stools
- Persistent vomiting
- Signs of dehydration (decreased urination, dizziness)
Remember, this information is for general knowledge and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor or other qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of diverticulitis.